- Publicatie 8 Januari 2022
![]()
Digital twins (DT), aiming to improve the performance of physical entities by leveraging the virtual replica, have gained significantgrowth in recent years. Meanwhile, DT technology has been explored in different industrial sectors and on a variety of topics, e.g.,predictive maintenance (PdM). In order to understand the state-of-the-art of DT in PdM, the paper focuses on the recent advances of how DT has been deployed in PdM, especially on the challenges faced and the opportunities identified. Based on the relevant research efforts recognised, we classify them into three main branches: 1) the frameworks reported for application, 2) modelling methods, and 3) interaction between the physical entity and
virtual replica. They intend to analyse the techniques and applications regarding each category, and the perceived benefits of PdM from the DT paradigm are summarized. Finally, challenges of current research and opportunities for future research are discussed especially concerning the issue of framework standardisation for DT-driven PdM, needs for high-fidelity models, holistic evaluation methods, and the multi-component, multi-level model issue.
![]()
Author: Yingchao, Chong Chen , Fu Hu, Ying Liu and Ze li Source: Science Direct
Industry 4.0 is a new modernisation and computerisation trend of manufacturing driven by the advances of the Industrial Internet of things, cloud computing, edge computing and artificial intelligence [1]. The new paradigm promotes the adaption of these advanced technologies into the process and equipment in industrial manufacturing. Predictive Maintenance (PdM) is a critical component of Industry 4.0 content. As production activities deeply rely on machines states, maintenance has obtained critical importance. To avoid an unexpected breakdown, there is a transformation from reactive maintenance to proactive maintenance. Pdm is regarded as a cost -saving method, which aims to decide the maintenance tim for equipment before the upcoming equipment failure bu assessing the degradation condition and calculating the remaing Usful Life(RUL)
With the implementation of PdM, the unplanned downtime cost can be reduced. According to the report from McKinsey, the maintenance cost will significantly reduce by 18%-25% after implanting the PdM, and therefore the research on PdM appealed to lots of attention from both academia and industry in recent years. Nowadays, large volumes of data that contain valuable information about the process and operations can be collected from industrial equipment. Industrial data are collected by heterogeneous sensors and then stored in the database. Data-driven methods are employed to analyse this data and get valuable insights for prognosis.
![]()
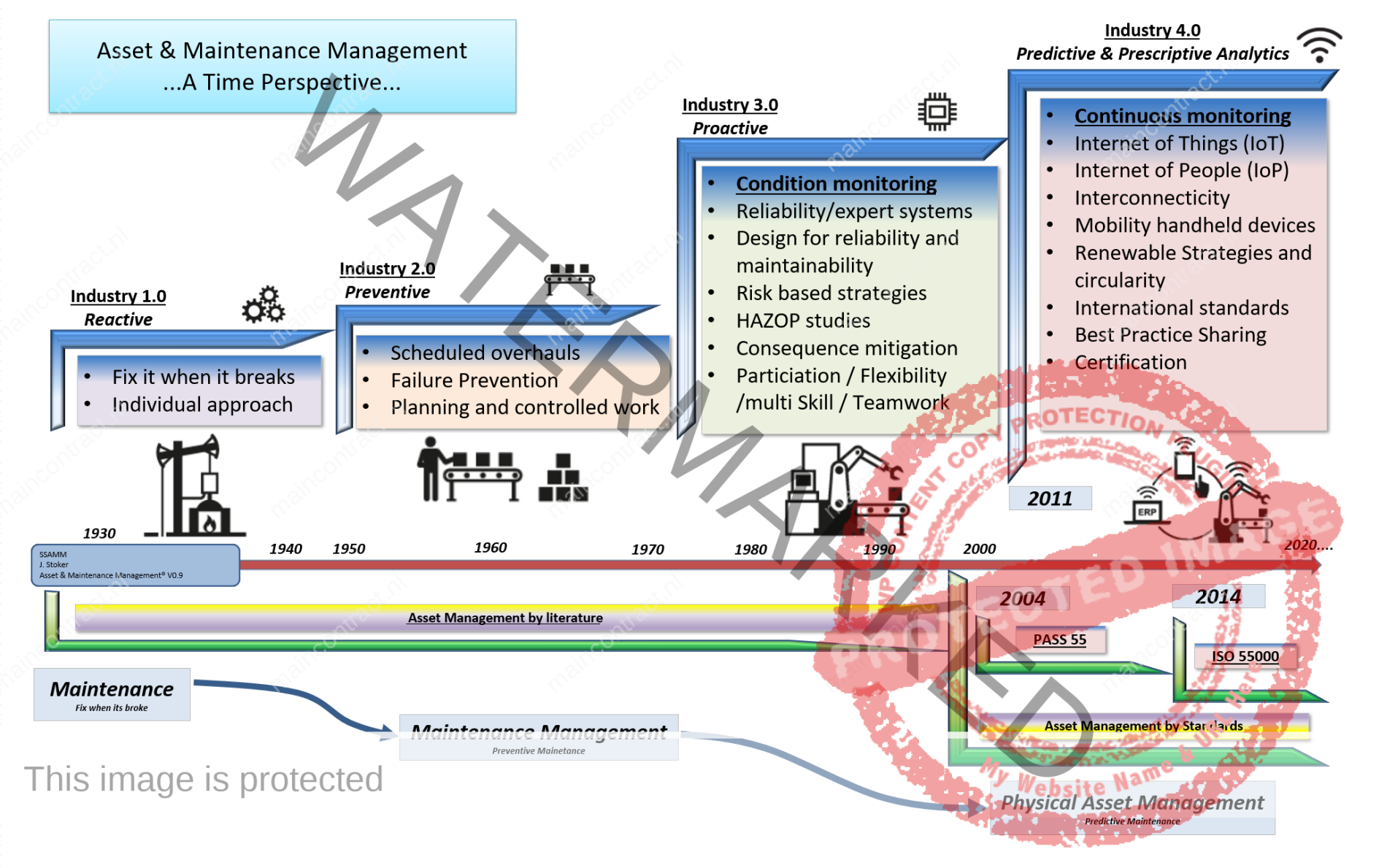
Click to enlarge: Asset & Maintenanec Management-A time perspective by Jan Stoker
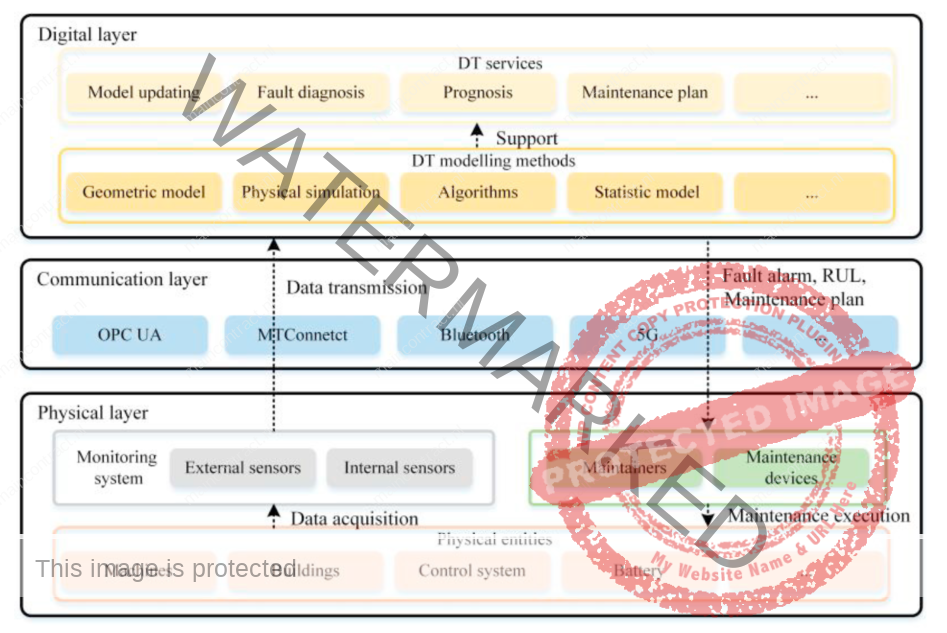
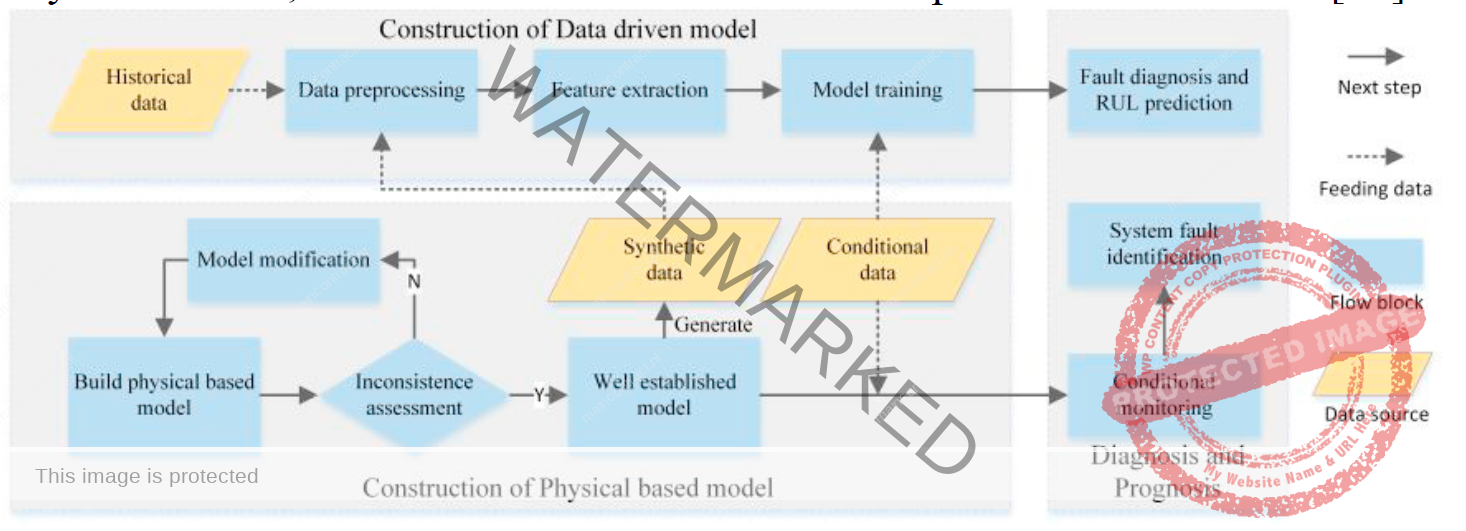
Typically, data-driven methods have two main scopes: machine learning approaches, and statistical approaches. Another mainstream method in PdM is the physical based model, which assesses the degradation of components using physics laws. Besides, the hybrid approaches, which is a combination of data-driven methods with physical-based methods, is the third class of PdM methods. With the development of sensor technology, AI, data science, and IoT, a new paradigm for engineering is developed, named digital twins (DT), which mainly consists of a physical entity, digital replica, and the connection.
DT is targeted at improving the performance of the physical entity leveraging the analysis of the virtual counterpart. DT is of importance in engineering by some scholars. Tao et al. deemed that DT is a critical enabler towards Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing. The research about DT is still in its primary. The main content of the current research is the concept, characteristics and framework of DT. Furthermore, DT is widely deployed in the product life cycle from the concept design to the logistic. Especially, the publication about the DT- driven PdM emerged and saw rapid growth in recent years. As a new technology, DT attained a growing interest, which arises a need to make it clear state-of-the-art in terms of concept, application, technology.
![]()
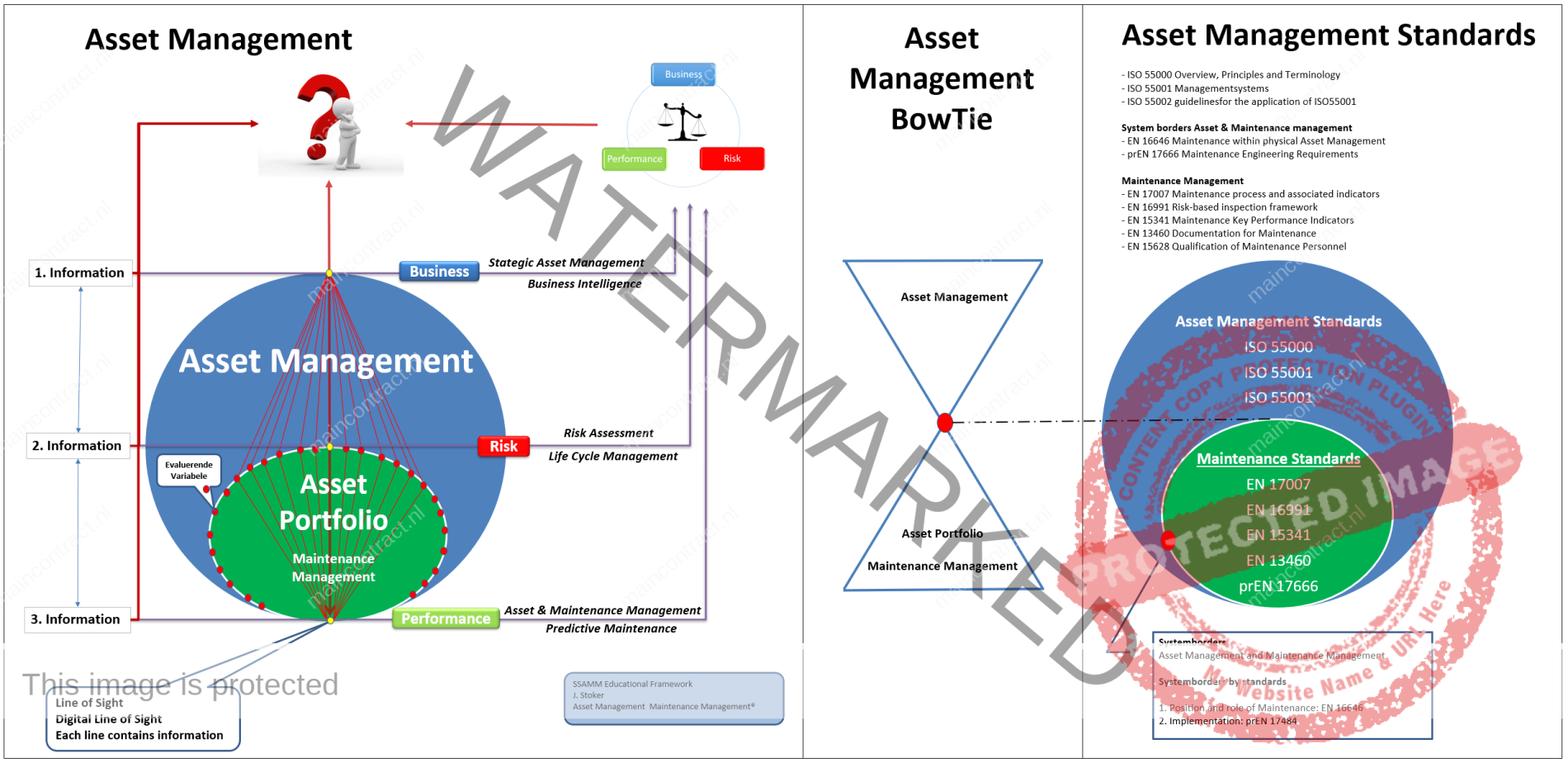
The recently published standard EN 17485 introduces methods and procedures about maintenance within physical asset management for all the levels and functions of the organizations’ management, including corporate planning management, plant management, technical management, production management, financial management, asset management, maintenance management, and quality management. Further and maybe even greater benefits are now being found through improved credibility in the eyes of customers, regulators and other stakeholders.
Click to enlarge
Physical asset management also results in much greater engagement and motivation of the workforce, and in more sustainable, continual improvement business processes. Physical asset management builds up the required link between maintenance management and the organizational strategic plan and gives direction to maintenance activities.The standards EN 16646 and EN 17485 build the bridge between ISO 5500x (Asset management system standards) and the EN maintenance standards. ISO 55001 states that organizations should determine e.g. the organizational context, requirements for the assets, decision criteria, strategic asset management plan and asset management plan (including maintenance).
However, it does not describe how to do it. Respectively, maintenance standards often introduce e.g. the concept of the required function or the concept of maintenance strategy, but do not explain how they have been determined. EN 17485 introduces a methodological framework which advises organizations to implement the requirements presented in ISO 55001. By doing this it creates the bridge between the several maintenance standards and ISO 5500x in order to give an applicable starting point to the more detailed documents for the specific sub-functions of maintenance (See AM-BowTie).
This insights, the Asset Management BowTie, can be added toward the Asset Management paradigm with the (Digital) Line of Sit. To add the BowTie principle, the body of thoughts of the EN-17485 can be incorporated in the Asset Management paradigm with the mentioned standards. Result is a deepened figure 1 of the ISO5500 completed with the Line(s) of Sights, the levels of information, Business, Risk Assessment and Asset & Maintenance going to decision making in balancing Costs, Risks and Performance.
Click to enlare Asset Management BowTie: See Body of thoughts AM-BowTie Click Here
![]()
Although predictive maintenance is one of the important topics in the DT area, there lacks a common understanding of the trend, challenges and opportunities in both industry and academia. DT brings a new engineering solution for PdM, while the technological improvement and performance variation for a system in the new paradigm is not clear.
Besides, to the best of our knowledge, there are two papers that reviewed the development of maintenance and DT, and the advances of DT for PdM has not been reported. Thus, a summary of the recent advance of PdM facilitating by DT is needed. In this paper, a systematic review for publications about PdM and DT is conducted where the trend is discussed to recognise research gaps and opportunities.
![]()
5. React, Discuss & Article
Discuss or give your opinionFollow on FacebookFollow on Twitter
Related Articles
Tags: Circulair