Pagina Inhoud
The research is focused on the role of Maintenance Management as one of the four fundamental basis of Assetmanagement as defined in the NEN-ISO 55000. The organization’s objectives, level of performance costs and risks are defined in the Strategic Asset Management Plan (SAMP) and Asset Management Plan(s) (AMP). Both descriptions are important documents and needed in te situation when maintenance management is outsourced. The information as described in the SAMP/AMP describes the Maintenance Strategy. The research want to provide in understanding how the SAMP and AMP can be defined and described. The scope of the research includes the three types of element structures considerd from the inheritance wich are Civil, Building and Industrial elements and components. Based on a teh ‘Assetmanagement union’ paradigma wich contains the ‘Line of Sight’ the organization policy and goals can be connected with the components os the Asset. This article is a deepening and expansion of the Strategic Asset Management Plan previously posted mid-October 2016. Added are the levels 1 and 2 of the SAMP / AMP.
- Draft Version: 17 June 2014
- Updated December 3, 2015
- Updated February 8, 2017
- Updated 23 september 2017
Gebaseerd op SAMP publicatie Oktober 2016 (Klik Hier)
![]()
![]()
Author: ing. Jan Stoker MSc. MEng.
The research explores the SAMP/AMP, what is a SAMP/AMP, what is included and to what extent it providing a framework for the creation, implementation and finalization of Maintenance strategies like Maincontracting or Integrated Performance Contracts. The research is not restricted to the variables that make up a SAMP/AMP but all 39 (thirty-nine) Evaluating Variables based on ‘The line of Sight’ This has led to a SAMP/AMP on three abstraction levels related to the for the three organizational levels (Strategic, Tactical and Operational)
The chosen research approach to achieve a SAMP/AMP is the Delphi research method. Reason for this research type is that teher are no (yet) standard procedure is to establishement a SAMP and how it should look within the framework of the research. The outcome has led to insights into the framework of the maintenance concept Maincontracting but ook how the policy can be linked to the smallest part of the asset That Ultimately the framework is guaranteed as in Figure 1. This body of thoughts represents in the ‘Line of Sight’ (Click here)
Reason to propose a SAMP / AMP is an insight/result from the research shows that is not always is clear which organization objectives or expected performance or client defined in the Maintenance Contract. The organization aims and achievements are not always communicated as such by the contractor or defined in the contract. For that reason, considered the thirty-nine variables defined and quantified to use this information tte in Phase Contract Formation and Contract Realization phase.
Figuur 2 : Click To Expand The Line of Sight.
1. The result: A SAMP on three levels
The result is a SAMP/AMP at three levels of abstraction. At the highest level, the SAMP abstract and concisely defined and is intended for the entire organization as a communication tool and a generic basis. For example, the tick the internal-and external context and the technical quality must be guaranteed alongside the primary process goes on happening in the Asset, typical characteristics of the asset and maintenance goals.
On the second level is the SAMP/AMP basically defined on the basis of the 39 (thirty-nine) variables. The variables are defined on the second level of abstraction and quantified. It is, however, indicates a broadening and deepening of the abstract document on the basis of the 39 (thirty-nine) variables where the organization is all about but also the context between the Asset Management System and the Asset Portfolio.
On the third level are the 39 (thirty-nine) variables completely defined and quantified the difference in goals. The latter is significant because a variable number of questions, each giving their own disparate goals insight into the outcome.
Limited Summary SAMP
The technical management and maintenance is contracted with the concept Maincontracting. This means that the contractor is responsible and competent in its activity to fill in ensuring the technical condition and the continuity of the primary process that takes place in the object. The frameworks and principles have been laid down in the Strategic Asset Management Plan (SAMP). On the basis of an investigation Delphi the SAMP is arranged. The Delphi worked with financial and policy leaders, operational managers and contract managers. Actually three groups representing the owner, performers and (internal) customers
The outcome of the research is summarized in nine subjects. These issues provide a high level of abstraction framework and starting point for the Maincontractor again. For example, the technical fitness level fixed for the life of the asset, are defined organizational objectives of the client, the structure of auditing and documented maintenance. What typifies the SAMP is that a number of activities during the investigation will determine the contract implementation phase.
During the authentication allows the contractor fixed on the basis of symptoms of faults which determine whether or not the contract price, and the MJOB be valid. In addition, the contractor fixed on the basis of standardized methods determine the critical and non-critical construction, installation -and its parts. preventive and corrective maintenance activities shall be determined on the basis of risk assessment and implemented. A feature of this approach is that the contractor have knowledge of the financial risks and can anticipate this by building, -and set out to make the contract. A result that can be adjusted transparently KPIs and SLAs.
Figure 2: The SAMP provides insight into the life of the asset is within the lifetime of an asset. (Click to enlarge)
2. The Research Approach: Delphi
The SAMP has been realized on the basis of the Delphi method. The aim of the Delphi study is the view and understanding of stakeholders and / or experts on the Asset Management to collect in a systematic manner and process. It is basically an interactive communication protocol between the researcher and the participants. Based on the Delphi Research created a joint opinion without interaction can influence the process and the outcomes. It is a structured form of group interview in qualitative research. By different officers each his / her own responsibility and authority questions and to submit subjects obtained understanding what the principles are and how the framework is formed.
In the first phase, individually or in groups to the participants, mostly experts, a question submitted with the request to respond. The researcher summarizes the responses together and draw conclusions from that. This report he lays back to participants for feedback, sometimes in a group discussion, sometimes individually. In the report, the investigator may possibly even send some depth questions. This process is repeated until a certain consensus has been reached, or a clear response was found at the research question.
- Formulate propositions and topics
- Theorems and topics to present to participants
- Opening of the group consulting problem
- Participants formulate first answer
- Researcher collects responses and summarizes
- Summary circulated
- Participants respond, complement and reconsider first answer.
3. The procedure
In the process model the same process steps are displayed and consists of seven process steps, namely:
- Research questions
- submit
- Analysis
- Conference call
- Process
- review
- final
Of each process step are some examples of the issues identified and their subjects.
- Press “previous” or “next” to go to the next process step or press directly on the step.
- In each process step, you will find tabs in which the subjects are grouped.
- the subjects are appointed by their questions and sub-questions per tab. Press tabs to view each tab
- Red colored words are provided with a definition; press the red words.
- Below procespannel is responsive and the most optimal view with a laptop or desktop.
Process Step 1 “Research Questions”
In an initial consultation with an official responsible for the Asset compiled the research. Primary goal is to give the research an understanding of the principles for drawing up the Maincontract.
Below are the research questions formulated in four separate tabs displayed.
-
- What should the technical condition of the asset throughout life
- There must be led by the client on site
- Who manages the documented information
- Are the organization’s objectives are incorporated in the contract
- Should the Asset Management Objectives are included in the maintenance contract
- The asset management plan is the responsibility of the client
- The Asset Management System is part of the maintenance contract
- Vervaningsbudget belongs to the contract
- Include facility management and / or technical activities belong to the contract
- What is the definition of a maintenance contract
- Substitutions in order to ensure the functionality and performance are among the contract price
- The contractor is responsible for the maintenance strategy
- The contractor is responsible for the maintenance management
- The contractor is responsible for the maintenance objectives
- The contractor is responsible for maintenance
- The contractor is responsible for auditing compliance with the BS 19011
- To what extent is the competence weighted by the client
- the extent to which the competence is weighed by the contractor
Figuur 3: Growth Asetmanagement & Maintenance (Click to expand)
Proces diagram (1)
Process Step 2 “Submit”
The formulated research questions are presented to the group officials. The aim is to enable the firm or the questions are valid and are a response to compile SAMP, what is contracted and what are the award criteria.
To determine this, and a research question an AHP analysis that the alternatives can be weighed should each research question the goals, alternatives and criteria to be determined. The following statement by the research question defined the objectives, alternatives and criteria.
Below are four separate tabs each main topic, the issues and questions listed with their goals and sub-goals. Press the “+” sign to open the subject.
In this example, two of the twenty-nine subjects have been appointed. Not all questions and alternatives are illustrated in this example. In this example, two of the five topics have been appointed. Not all questions and alternatives are illustrated in this example.
Proces diagram (2)
Processtap 3 “Analyse”
The substantive response will be analyzed by the researcher. The results are described and summarized.
This results in a framework in which the research play on the concept Maincontracting and a common response to the research.
Processchema (3)
Processtap 4 “Group Conversation”
In a group conversation the results wil be submitted. Based on the results there will be presented a written analayse. The group will react on the will their opinion based on arguments.
Proces diagram (4)
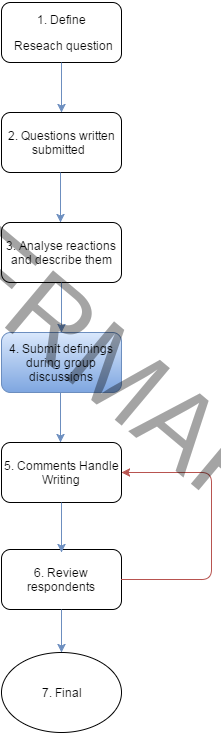
Processtap 5 “Process”
The research questions are answered in two ways. The reactions and results of the conference are described. the subjects are also “weighed” on the basis of AHP analysis. This creates beside the picture why one finds something of a particular subject an organization to the degree of importance.
The latter can be crucial when it comes to decision-making and prioritization. These issues are taken policy and have an impact within the framework that is defined within the Asset Management.
Proces diagram (5)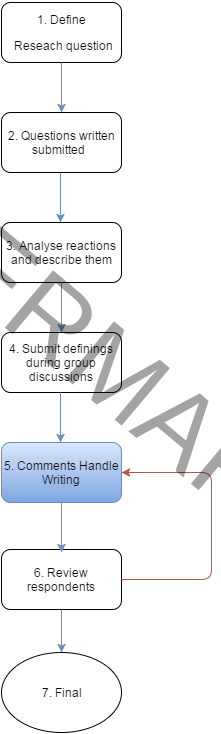
Processtap 6 “Review”
The results set out in stage 5 are submitted to the group whether the group can identify with what has been established. In particular, the focus will be on how to prioritize the issues on which the decision is based.
Proces diagram (6)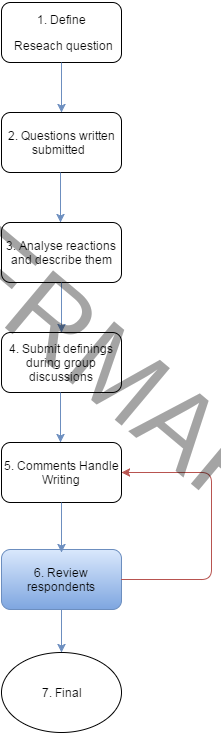
Processtap 7 “Final”
On the basis of the responses that have been given or agreement which may be identified by respondents were group. Based on the quakes conclusions can be drawn.
Proces diagram (7)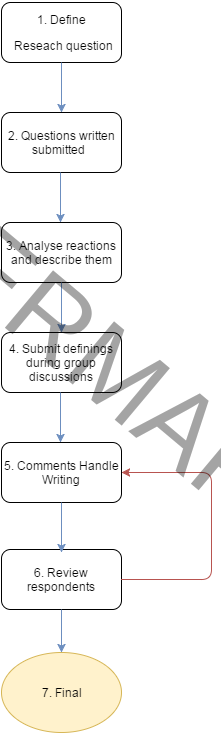
4. Results & insights
Results of the used method is a description of the SAMP/AMP in three levels. Each level has his own definition and defines specific goals, expectations and performance.
- Level 1 defines the scope and abstract principle of the portfolio and is based on Level 2.
- Level 2 in more detail, in which all the thirty-nine have been processed textual. By processing the thirty nine variables in the text within the context of the research arises description that has a certain degree of consistency because the definitions of the thirty-nine variables are used as the basis of the Delphi analysis. Level 2 is based on level 3.
- Level 3 defines and quantifies each variable targets and selects the alternatives. The targets are determined on the basis of the Delphi analysis and organized according to AHP. Level 3 is the basis and foundation for the levels 1 and 2.
In fact, levels 1 and 2 aggregation of the choices and outcomes Level 3, however, specifically written for those who need to define the maintenance contract.
4.1 The two aggregation levels of the SAMP
Level one is an abstract description of the results of the third level and intended to define the scope and premise without substantive knowledge of the variables. More insights, description and delve into the context of the theoretical framework takes place at level 2. The thirty-nine variables literally used as fundamental framework for the SAMP/APM. Level 2 is a basic description as the objectives, expectations and performance is defined in terms of the variables specific definition as defined in ISO 55000. Based on their definitions as defined in the NEN-ISO 55000 the results of Level 3 defines the roll and the starting point of both levels. By using the Delphi and Analytic Hierarchy Process the thirty-nine variables wil be defined and can be used for both other levels.
4.2 The SAMP Level 1 & 2
In the following sections levels 1 & 2 of the SAMP and AMP wil be described. However, the Asset has to made anonymous but are maintained its typical properties and characteristics like :
- The Asset has a monumental designation
- In and outside the Asset there are critical processes that influence the social, political en economic environment
- The asset was recently renovated but remained its characteristic features of the interior and exterior preserve
4.2.1 Level 1 SAMP
The SAMP of Level 1 is designed to provide insight into the organization’s objectives towards the context (Internal and External) and basics to establish the maintenance contract.
4.2.1.1 ‘The Asset’
The Strategic Management Plan is documented information that describes three fundamental principles of the Asset. These are :
- How organization objectives can be transformed into asset management objectives,
- What is the approach for developing Asset Management Plans
- And the role of the asset management system to assist in achieving the asset management objectives
Those three areas are the framework and fundamentals of the Maintenance Management. By formulating the, defining and quantifying the subjects it is possible to create the intende Maintenance Contract. This does not mean in detail there at the element level aesthetics, functionality and performance is defined but a framework that indicate these three concepts within the context of asset management and technical management and maintenance.
4.2.1.2 Organizational Goals
The asset owner manages a diversity of Assets. The technical management and maintenance of these Assets will in some cases rather than using the concept Maincontracting. Under the concept Maincontracting is understood that one contractor is responsible for the technical management and maintenance through integrated performance. The delivered performance of the contractor is to ensure the design-and performance requirements of construction, -and installation parts.
The framework and basis of the technical management and maintenance is established in the Strategic Asset Management Plan (SAMP) drawn up by the client and is guaranteed by the contractor.
4.2.1.3 Local organization
There is a local organization of the principal guide the management of the technical facilities and processes. Here, the process is a guiding facility and presents the technical process at the service of the facility process. As example can be used a demarcation of the elements used the Dutch regulation the so called ‘Regulations Task management’*
*The regulation is expired but stll valid as a example
4.2.1.4 Typical properties Asset
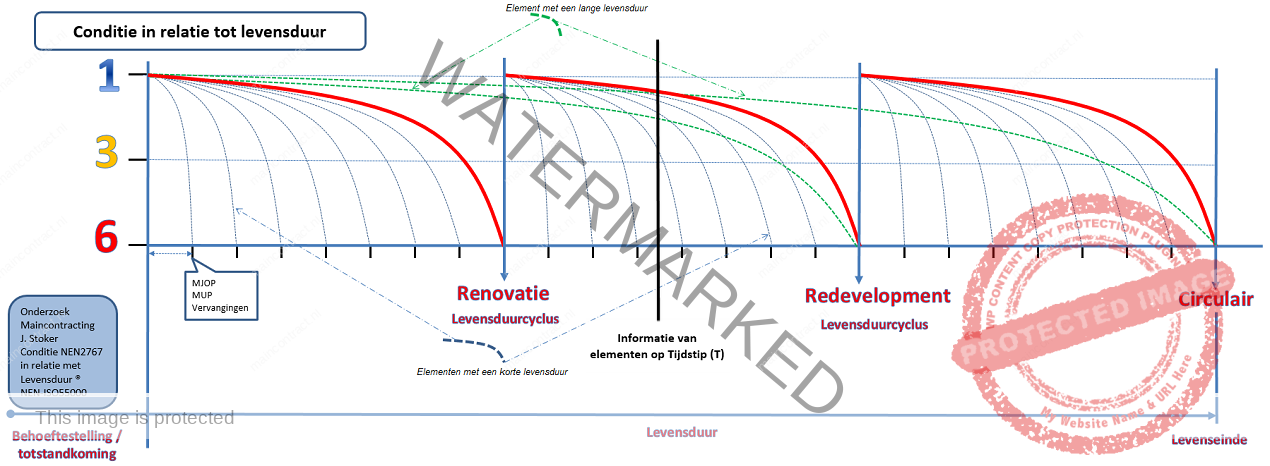
The Asset has some typical characteristics that affect the technical management and maintenance. Two characteristics are the asset itself and the process that takes place within the Asset. The asset has a monumental designation allowing specific laws and regulations apply on the face of the asset and integral components of this asset. The Asset also has a dominant role in geograpic lokation of the city and have critical processes that influence the social, political en economic environment. The historic designation implies that mutations of elements considered rather “may” find. The objective of the client is to provide the asset during the lifetime to maintain the technical condition level 3 as defined in NEN 2767, as shown in Figure 6. It is not ment to be that each element or construction, -and installation must be condition level 3 or maintan towards level 3. This may be waived as long as it fits within the parameters set by the landmark designation and does not disturb the primary process.
Figure 6: Lifetime and degradation
4.2.1.5 Primary process
Within the asset there are processes and functions that influence the social, political en economic environment. The processes an functions are seen as the primary process that takes place within the Asset. It may be risky if the primary process is disturbed technical, stagnant, or can not take place. Disruption, stagnation, or not being able to take place of the primary process is to be regarded as not desirable and should be prevented. Symptoms of defects (as defined in NEN 2767), which this may cause should be identified so that measures can be taken before faults occur. Risk identification takes place on the basis of the NPR-73 and ISO standards, that are controlled thereby.
4.2.1.6 The maintenance strategy, maintenance and maintenance goals
Technical management and maintenance ensures that the primary process can be carried out and maintained the typical characteristics of the asset. Based on the premise that disruption, stagnation or failure to take place of the primary proces is deemed not desrable and must be prevented. Symptoms of defects (as defined in NEN 2767), which this may cause should be identified so that measures can be taken before faults occur. Risk identification takes place based on the NEN-ISO 73, and the standards that are controlled thereby. By classifying elements in critical and non-critical can NEN-EN 13306 the maintenance strategy, maintenance objective, the maintenance and maintenance management defined.
4.2.1.7 Ensuring SAMP
The SAMP is ensured by the client and contractor auditing processes based on the NEN-ISO 19011. Auditing of all thirty-nine processes which form the framework and fundamentals of the SAMP, at periodic intervals and is the responsibility of the client. Necessary investments by the contractor performed annually in the form of a CAPEX budget as formulated in the NEN 2767.
4.2.1.8 Documented Information
All information regarding the maintenance and construction element, -and installation share is up to date once within three days of scope and updated systems of the client. The changes take place in accordance with a defined process in the systems of the client.
4.2.1.9 Contract price
Besides all related topics focus is on the two main components of the contract price. These are integral planned as well complete replacements are fixed in CAPEX budget and repairs to fail. The principle is that all replacements are among the contract. As a result, the contract is an integral part of the system of the items 5, 6 and 7. Specifically, symptoms of defective part of the named points. The reason for this approach is the chain efficiency, maximum responsibility and authority of the contractor and ensure the SAMP.
4.2.2 Level 2 SAMP
The object, hereafter referred to as The Asset24 , is an Asset type29 with a number of characteristic properties. A physical property of the asset is that it has a historic designation is part of the life cycle26 “just after renovation” and that in this asset there is an administrative activity (primary process) that affects the external environment in which the asset is located. The asset is part of the asset portfolio27 of the Asset Owner, however, stands out as asset type within the Asset Portfolio. These properties enable the frames to asset life25 and the continuity of the primary process. Within the context of the life aesthetics and technical condition should at least be kept in condition 3 set out in the NEN 2767 and the continuity to the critical asset components have a high degree of availability.
The primary process should not be disrupted causing risks21 construction, -and plant parts must be determined whether this critical30 or noncritical Asset parts. Identifying and qualifying risks takes place in accordance with the ISO 73 and executed by the client and contractor. The preventive and predictive measures of the Asset management31 and the remedies of the Asset managementsysteem39 to control the risks are aimed to ensure continuity.
Because the technical management and maintenance is outsourced16 in what could be described as a Main Contract preventive, predictive and corrective (measure) are processes19 next to the Asset Management System audited audited1 in accordance with ISO 19011. The main contract itself is defined as:
“Technical Maintenance Management concepts as Maincontracting is closing integrated performance contract between a client and the contractor as Maincontractor for the Technical Management and Maintenance of Assets. The client is responsible for the preparation of the Asset Management Plan. The Maincontractor is, within the framework of the Asset Management Plan, responsible for the Maintenance Management, empowered to align it with the customer / end user of the asset and is responsible for all services perfomances”
The the top management23 ensures that its policy18 , objectives12 and organizational objectives14 in the Asset Managementplan33 set. The Asset Management Plan which required activities, people, resources and time frames for reaching the objectives of the asset management organization. The framework and starting point of the Asset Management Plan is the Strategic AssetManagementPlan32 . Based on the documented information6 of the Asset Management Plan and the SAMP is realized, the procurement of the Main Contract. The Asset Management Plan and the SAMP. The Asset Management Plan indicated that a local organization working to present the stakeholders22 client and contractor. The client has a facility and technical contact for the asset provided. The technique is subordinate to the facility activities on behalf of the primary process. The Contractor represents and is part of the local organization. This local organization is responsible for the level of service36 with respect to the life and the primary process. The contractor is responsible effectiveness7 are capability2 and competent3 to turn in order to put in conformitt4 to realize the like is recorded in the SAMP. By audit ring in the form of monitoren9 and mesurement10 to be carried out to be effective in relieving symptoms of nonconformity11 identified to incident8 to avoid. Due to continues improvements5 are on the basis of symptoms of defects, preventive action34 , predictive action35 and corrective actions37 measures initiated and organizationalplans15 drawn up. In this way, ensures the contractor on the basis of the maincontract that the performance17, and requirements20 of construction, -and installation parts.
References :
- NEN-ISO 55000 Asset management – Overview , principles and terminology
- NEN-EN 13306 : Maintenance Terminology
- NPR-ISO Guide 73 Risicomanagement -Terminology
- NEN-ISO 31000 Risicomanagement- Principes en Guidelines
- NEN-ISO/IEC 31010 Riskmanagement – Risk Assessment Techniques
- NEN-ISO 37500 Guidance on Outsourcing
- NEN-EN 13460 Maintenance – Documentation for Maintenance
- NEN-EN 16646 Maintenance – Maintenance within physical Asset management
- Definition Maincontracting (Click Here)
De auteur thanks the NEN for his permission to publish the terms and definitions of the used standards
Discuss or give your opinionFollow on FacebookFollow on Twitter